The Science Behind
The CSIRO Total Wellbeing Diet was developed by scientists at the CSIRO and is considered one of CSIRO’s top 10 innovations in its 100-year history.
Since we went online in 2014 we have published a number of scientific reports that give insight into the nutritional status of the Australian population.
Our reports

CSIRO Total Wellbeing Diet 5 Year Report
One of the world’s largest weight loss studies reveals the key to three times more weight loss
January 2020 - View infographic or Download the full report
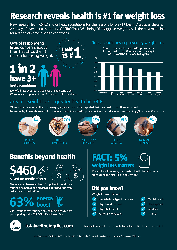
Research reveals health is #1 for weight loss
New research from CSIRO shows health conditions top the reasons for losing weight in an analysis of 65,000 dieters. A follow-up survey of 3000 members suggests weight loss is the best medicine for a range of chronic health conditions.
August 2019 - View infographic

Gut health and weight loss
An overview of the scientific evidence of dietary fibre for weight loss
January 2019 - Download the report
Total Wellbeing Diet Online Member Study
The aim of this study was to examine the weight loss of members who had completed at least 12 weeks on the TWD Online program
August 2018 - Download the report

VegEze Impact Report
How a mobile app is boosting vegetable intake in those that need it most.
June 2018 - Download the report


CSIRO Diet Types
An exploration of the personality traits of over 90,000 Australians
September 2017 - Download the report

TWD Online Program 1 Completer's Weight Loss
A scientific study of 5,594 members who have completed Program 1 of the CSIRO Total Wellbeing Diet.
June 2017 - Download the report

Fruit, Vegetables and Diet Score
A deep dive into the self-reported fruit, vegetable and juice consumption of 145,000 Australian adults. With Horticulture Innovation Australia.
April 2017 - Download the report

CSIRO Healthy Diet Score 2016
Australia's largest ever diet survey confirms we're not as healthy as we think we are
September 2016 - Download the report
CSIRO Total Wellbeing Diet scientific publications list
The diet has been extensively researched with results published in medical and nutrition journals internationally. See the list of publications below.
- Bowen J, Noakes M, Clifton PM. 2006. Appetite regulatory hormone responses to various dietary proteins differ by BMI status despite similar reductions in ad libitum energy intake. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 91(8):2913-9
- Bowen J, Noakes M, Clifton PM. 2005. Effect of calcium and dairy foods in high protein, energy-restricted diets on weight loss and metabolic parameters in overweight adults. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 29(8):957-65.
- Bowen J, Noakes M, Clifton P. 2005. Effects of dietary protein type on energy intake and appetite regulatory hormones. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 14. Suppl: S66.
- Bowen J, Noakes M, Trenerry C, Clifton PM. 2006. Energy intake, ghrelin, and cholecystokinin after different carbohydrate and protein preloads in overweight men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Apr. 91(4): 1477-1483. Jan 24.
- Brindal E, Freyne J, Saunders I, Berkovsky S, Smith G, Noakes M. Features predicting weight loss in overweight or obese participants in a web-based intervention: randomized trial. J Med Internet Res. 2012;14(6):e173.
- Brinkworth GD, Noakes M, Parker B, Foster P, Clifton PM. 2004. Long-term effects of advice to consume a high-protein, low-fat diet, rather than a conventional weight-loss diet, in obese adults with Type 2 diabetes: one-year follow-up of a randomised trial. Diabetologia. Oct. 47(10): 1677-1686.
- Clifton PM, Keogh JB, Foster PR, Noakes M. 2005. Effect of weight loss on inflammatory and endothelial markers and FMD using two low-fat diets. Int J Obes (Lond). Dec. 29(12): 1445-1451.
- Farnsworth E, Luscombe ND, Noakes M, Wittert G, Argyiou E, Clifton PM. 2003. Effect of a high-protein, energy-restricted diet on body composition, glycemic control, and lipid concentrations in overweight and obese hyperinsulinemic men and women. Am J Clin Nutr. Jul. 78(1): 31-39.
- Keogh JB, Grieger JA, Noakes M, Clifton PM. 2005. Flow-Mediated Dilatation Is Impaired by a High-Saturated Fat Diet but Not by a High-Carbohydrate Diet. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25(6):1274-9
- Luscombe-Marsh ND, Noakes M, Wittert GA, Keogh JB, Foster P, Clifton PM. 2005. Carbohydrate-restricted diets either high in monounsaturated fat or high in protein are equally effective at promoting fat loss and improving blood lipids. AJCN. Apr. 81(4): 762-772.
- Moran LJ, Brinkworth G, Noakes M, Norman RJ. 2006. Effects of lifestyle modification in polycystic ovarian syndrome. Reprod Biomed Online. May. 12(5): 569-578. Review.
- Moran LJ, Luscombe-Marsh N, Noakes M, Wittert GA, Keogh JB, Clifton PM.2005. The satiating effect of dietary protein is unrelated to post-prandial ghrelin secretion. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 14. Suppl: S64.
- Moran LJ, Luscombe-Marsh ND, Noakes M, Wittert GA, Keogh JB, Clifton PM. 2005. The satiating effect of dietary protein is unrelated to post-prandial ghrelin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 90(9):5205-11.
- Moran LJ, Noakes M, Clifton PM, Wittert GA, Williams G, Norman RJ. 2006. Short-term meal replacements followed by dietary macronutrient restriction enhance weight loss in polycystic ovary syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr. Jul. 84(1): 77-87
- Moran LJ, Noakes M, Wittert GA, Clifton PM, Norman RJ. Weight loss and vascular inflammatory markers in overweight women with and without polycystic ovary syndrome. Reprod Biomed Online. 2012;25(5):500-3.
- Moran LJ, Noakes M, Clifton PM, Wittert GA, Williams G, Norman RJ. 2005. Effective weight loss and maintenance strategies in polycystic ovary syndrome. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 14. Suppl: S94.
- Noakes M, Clifton PM. 2004. Weight loss, diet composition and cardiovascular risk. Current Opinion in Lipidology. 15: 31-35.
- Noakes M, Bowen J, Clifton P. 2005. Dairy foods or fractions for appetite and weight control. Aust J Dairy Tech. July . Pp.152-153.
- Noakes M, Lau CW, Bowen J, Clifton PM. 2005. The effect of a low glycaemic index (GI) ingredient substituted for a high GI ingredient in two complete meals on blood glucose and insulin levels, satiety and energy intake in healthy lean women. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 14. Suppl: S45.
- Noakes M, Foster PR, Keogh JB, Clifton PM. 2005. Post prandial glucose and insulin responses to test meals and insulin sensitivity after weight loss on a very low carbohydrate diet compared to low fat high carbohydrate diets. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 14. Suppl: S112.
- Noakes M, Foster PR, Keogh JB, James AP, Mamo JC, Clifton PM. 2006. Comparison of isocaloric very low carbohydrate/high saturated fat and high carbohydrate/low saturated fat diets on body composition and cardiovascular risk. Nutr Metab (Lond). Jan. 11:3(1): 7.
- Noakes M, Keogh JB, Foster PR, Clifton PM. 2005. Effect of an energy-restricted, high-protein, low-fat diet relative to a conventional high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet on weight loss, body composition, nutritional status, and markers of cardiovascular health in obese women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. Jun. 81(6): 1298-1306.
- Noakes M, Williams G, Keogh JB, Clifton P. 2005. Influence of high protein snack foods on satiety, food intake and glucose and insulin response: a single blind cross over study. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 14. Suppl: S113.
- Parker B, Noakes M, Luscombe N, Clifton P. 2002. Effect of a high-protein, high-monounsaturated fat weight loss diet on glycemic control and lipid levels in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. Mar. 25(3): 425-430.
- Pearce KL, Clifton PM, Noakes M. Egg consumption as part of an energy-restricted high-protein diet improves blood lipid and blood glucose profiles in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Br J Nutr. 2011;105(4):584-92.
- Shrapnel B, Noakes M. Discriminating between carbohydrate-rich foods: A model based on nutrient density and glycaemic index. Nutr Diet. 2012;69(2):152-8.
- Sjoberg N, Brinkworth GD, Wycherley TP, Noakes M, Saint DA. Moderate weight loss improves heart rate variability in overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes. J Appl Physiol. 2011;110:1060-4.
- Stuart KL, Wyld B, Bastiaans K, Stocks N, Brinkworth G, Mohr P, et al. A telephone supported cardiovascular lifestyle program (CLIP) for lipid reduction and weight loss in General Practice patients: A randomised controlled pilot trial. Public Health Nutr. 2012;In Press.
- Taylor PJ, Kolt GS, Vandelanotte C, Caperchione CM, Mummery KW, George ES, et al. A review of the nature and effectiveness of nutrition interventions in adult males – a guide for intervention strategies. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Activity. 2013:10-13.
- Tey SL, Brown RC, Gray AR, Chisholm AW, Delahunty CM. Long-term consumption of high energy-dense snack foods on sensory-specific satiety and intake. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95(5):1038-47.
- Thomson RL, Brinkworth GD, Noakes M, Clifton PM, Norman RJ, Buckley JD. The effect of diet and exercise on markers of endothelial function in overweight and obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Human Reproduction. 2012;27(7):2169-76.
- Wycherley T, Brinkworth G, Clifton PM, al e. A one year high protein, low fat weight loss diet improves body composition and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight males Faseb J. 2012;26.
- Wycherley TP, Brinkworth GD, Clifton PM, Noakes M. Comparison of the effects of 52 weeks weight loss with either a high protein or high carbohydrate diet on body composition and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight and obese males. Nutrition and Diabetes. 2012;2:e40.
- Wycherley TP, Buckley JD, Noakes M, Clifton PM, Brinkworth GD. Comparison of the effects of weight loss from a high protein vs. standard protein energy restricted diet on strength and aerobic capacity in overweight and obese males. Eur J Nutr. 2012;52(1):317-25.
- Wycherley TP, Mohr P, Noakes M, Clifton PM, Brinkworth GD. Self-reported facilitators of and impediments to maintenance of healthy lifestyle behaviours following a supervised research based lifestyle intervention program in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetic Medicine. 2012;29(5):632-9.
- Wycherley TP, Moran LJ, Clifton PM, Noakes M, Brinkworth GD. Effects of energy restricted high protein, low fat vs. standard protein, low fat diets: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;96(6):1281-98.
